
The physical findings for diagnosis of a myofascial trigger point are (1) palpation of a tender nodule in a taut band, (2) a referred pain pattern specific for the muscle, (3) a local twitch response (LTR) with snapping palpation or triggering with needle, and (4) restricted ROM (Travell J, Simons DG, Myofascial pain and dysfunction: the trigger point manual, vol 1. Kennedy, who at the time was using crutches due to crippling back pain and was almost unable to walk down just a few stairs. In her private practice, she began treating Senator John F.
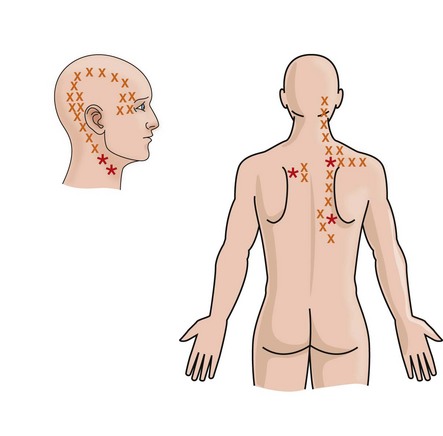
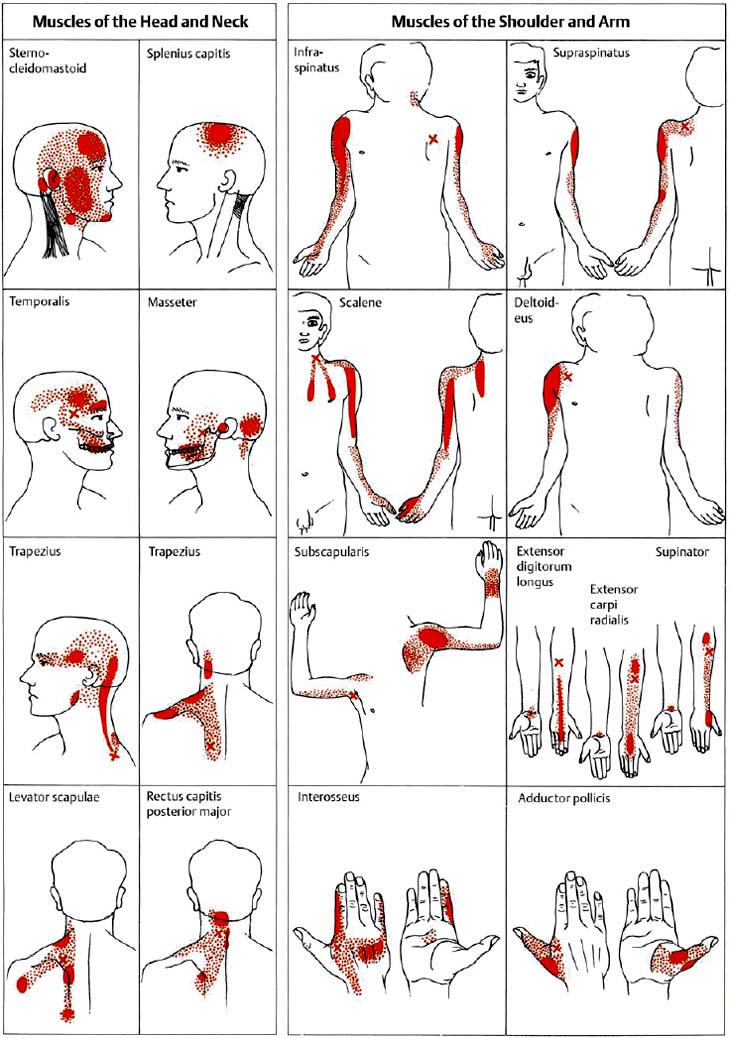
Active TrP produce a referred pain pattern specific to that muscle spontaneously and when the TrP is palpated. Travell pioneered and researched new pain treatments, including trigger point injections. Travell and Simons9 assumed that MPS could arise from activation of. Ge and colleagues used the Travell and Simons recommendations for finding a MTP. Travell & Simons’ Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual. The locations of active MTPs in FM subjects were generally found to be the site of latent MTPs in the controls. Relieve your supraspinatus pain and get rid of its trigger points by applying a simple self-massage.
#Travell and simons referred pain manual
Latent TrP are associated with stiffness and restricted ROM but no pain unless palpated. The acupressure of TP remotely evokes pain referred to in the so-called target area. Manual stimulation of active MTPs in FM produces a local and referred pain pattern that is similar to the subjects current spontaneous pain report. Trigger points (TrP) can be latent or active (Simons DG, Travell JG, Postgrad Med 73:66–108, 1983). The diagnosis of MPS is based on the presence of 1 or more trigger points. Select Symptom Area Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. Therapy can make use of various choices: anesthetic block of trigger points, stretch and spray, localized pressure at the level of TP, non-steroidal analgesics and adjuvants such as octreotide by endocular route and active physical therapy.Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) as defined by Travell and Simons is characterized by trigger points (TrP), limited ROM of the affected muscle(s), and neurologic symptoms (autonomic, proprioceptive) (Simons DG, Travell JG, Postgrad Med 73:66–108, 1983). acteristically referred from myofascial trigger points (TPs) that are From Travell JG and Simons DG: 'Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction. Few epidemiological studies have investigated the prevalence or incidence of myofascial trigger points. 4 Simons, David G., Travell, Janet G.,Travell & Simons’ Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual. The genesis of trigger points is multifactorial and includes morphological, neurotransmitter, neurosensitive and electrophysiological changes. Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is a musculoskeletal pain condition characterized by local and referred pain perceived as deep and aching, and by the presence of myofascial trigger points in any part of the body. Through palpation of muscle trigger points, Simons and colleagues. David Simons & Lois Simons,2nd edition, vol 1,1999 1 page 940. Referred pain is prevalent in the craniofacial region, and it would be helpful for. Sources: Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction, Dr.
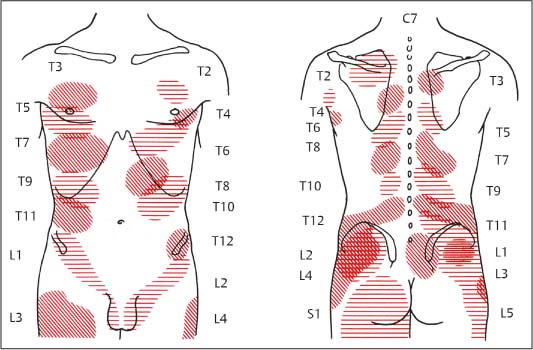
The acupressure of TP remotely evokes pain referred to in the so-called target area (or reference area) and a localized muscle contraction (twitch). As pain from such tender spots often is referred pain, you may feel pain in your back, groin or thighs, all of which originates in your abdomen.
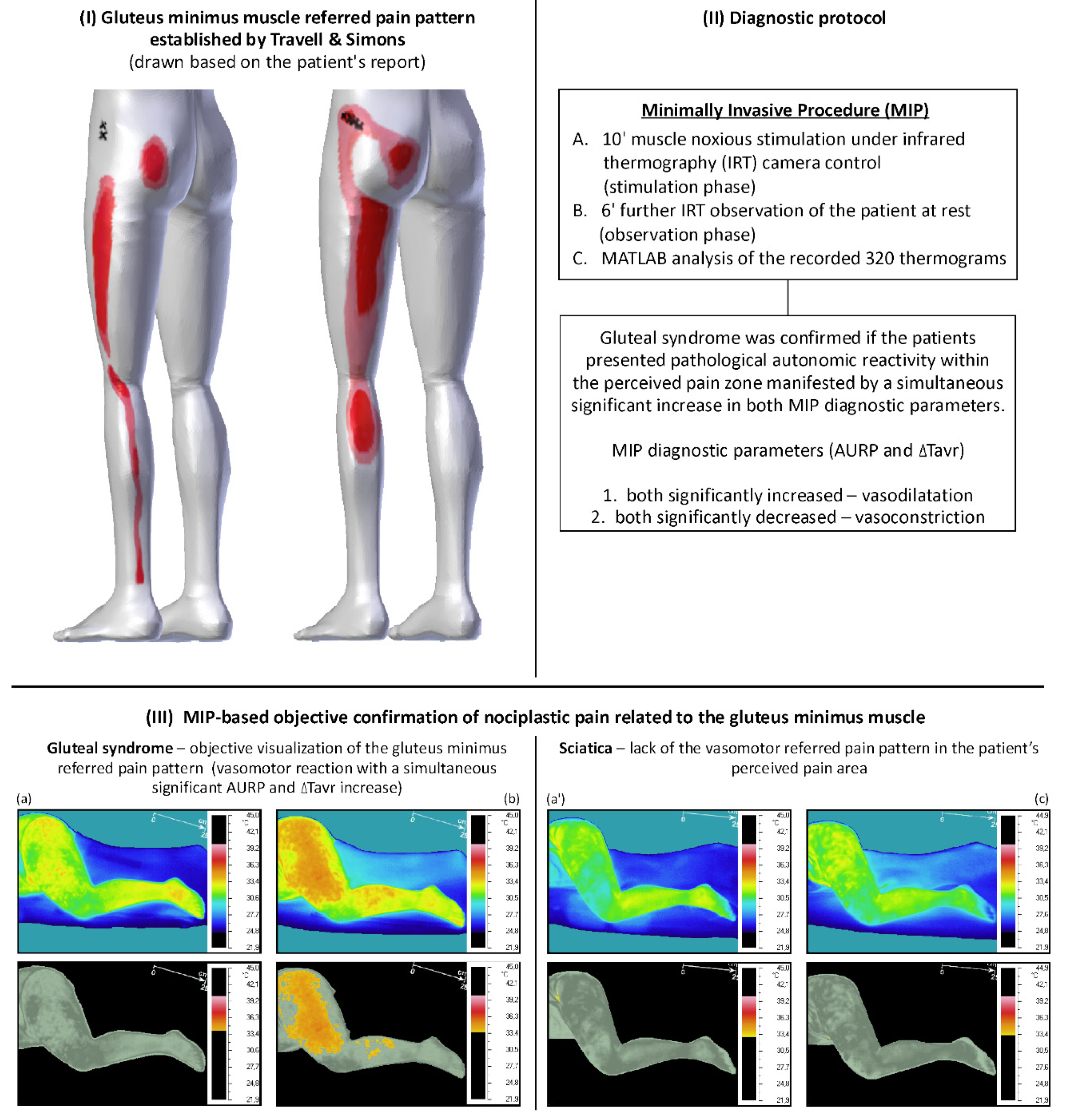
Moreover, measurements are obtained via dichotomous data (e.g., presence or absence of pain presence or absence of MTrP) or nominal data (i.e., no nodule vs. Trigger points (TP) are areas of hypersensitivity localized in one or more muscles that evoke pain referred to at a distance in the so-called target areas. In Travell and Simons’ MTrP-centered model of myofascial pain, the diagnostic criteria and relevant clinical findings can only be studied descriptively, using patient-reported outcomes. Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a condition characterized by local pain is reportedly, described as dull and deep, determined by the presence of myofascial trigger points. Overuse musculoskeletal pain affects 33% of adults and is responsible for 29% of work days lost due to illness. In this updated pain model, TrPs would be the primary hyperalgesic zones responsible for the development of central sensitization in CTTH. Summary Among the musculoskeletal pain syndromes, myofascial is certainly one of the most frequent. Referred muscle pain: clinical and pathophysiologic aspects. Travell & Simons Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: Upper half of body David G. Based on available data, an updated pain model for CTTH is proposed in which headache can at least partly be explained by referred pain from TrPs in the posterior cervical, head and shoulder muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
